What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is not usually considered a serious problem in the medical field, but it can be difficult to deal with because it can be unpleasant and embarrassing to deal with. Along with physical changes, a person with gynecomastia may also suffer from mental health traumas. The issue may resolve without the need for treatment, with a balanced diet and exercising but if it does not, medication or surgery may be suggested. Read on to learn more about the causes and symptoms of gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a condition that occurs in a male person. It
is generally referred to as “man boobs” or “man breasts.” It mostly develops in
newborn male babies, teenage boys going through puberty, and men in their older
ages. It is an increase in the size of breast gland tissues that changes the
appearance of the chest making it seem enlarged and puffy.
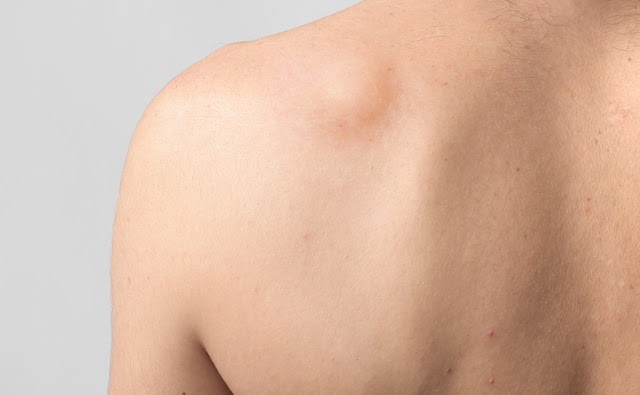
Gynecomastia can affect and cause swelling in one or both
breasts, and sometimes unevenly. Here, the chest of a male person may often
seem female-like. Although both males and females have breast tissues, these
aren’t noticeable in a male person until and unless they’re dealing with a
condition that causes their breast tissue to overdevelop and swell like
Gynecomastia.
There are plenty of reasons why this condition may develop
in a male person. It is generally caused by hormonal fluctuations in the body.
The increase in the level of estrogen and a decrease in the level of
testosterone may lead to the enlargement of male boobs.
While most people believe that estrogen is only produced by
a female, they know that males produce it in small quantities.
Other common causes of Gynecomastia are:
- Obesity, where a person gains excess weight that causes estrogen levels to rise leading to the expansion of breast tissues.
- Side effects of medicines
- Consumption of illegal drugs like cannabis, anabolic steroids, etc.
- Excess consumption of alcohol regularly
- Poor hygiene and a bad diet
- Health conditions like Liver damage and kidney failure
- Infection or tumors in the testicles
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
A person dealing with enlarged male breasts may start to
notice various symptoms of gynecomastia in their body, especially the chest
area. They may start to notice various symptoms of Gynecomastia like,
The growth of one or both breasts is the most common symptom
of gynecomastia. The swollen glandular tissue normally affects both breasts,
however, it can also affect just one.
About the nipple, breast growth can be consistent or
unequal. It may have a rubbery or stiff texture. The growth may emerge immediately
behind the nipple.
When touched, the breast or nipple may be uncomfortable or
tender.
A breast bud the size of a quarter or nickel may be present
in one or both breasts in boys. These are prevalent in boys during puberty, and
they can last up to two years.
It’s critical to distinguish between gynecomastia and male
breast cancer. Only one breast is usually impacted when cancer is present, and
the tissue is not always hard or firm. Dimpling of the skin, nipple discharge,
nipple retraction, and swollen lymph nodes beneath the arms are all signs of
cancer.
A breast abscess is another condition that can cause male
breast enlargement; however, this is not very common in men. Fever or chills
may occur in those who are affected. The swelling may be quite painful and hot
to the touch, and the skin around it may appear reddish.
Treatment for Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia normally goes away without treatment, but if
the reason is an underlying health problem like liver illness or hypogonadism,
the problem must be addressed before the breast symptoms go away. When there is
no obvious reason for gynecomastia in teenagers, a doctor may recommend
assessments every three to six months to see if symptoms are improving.
Treatment may be required if the condition does not improve after two years or
if it is causing substantial discomfort or humiliation. An anti-estrogen or an
aromatase inhibitor, for example, maybe prescribed to correct the hormone
imbalance.
If a patient’s symptoms persist after monitoring or initial
treatment, surgery may be recommended. Liposuction may be suggested to remove
the fat from the breasts or mastectomy may be recommended to get rid of the
breast gland causing the enlargement.
Book Free Consultation
Gynecomastia isn’t usually linked to long-term issues, but
those who develop it have a five-fold increased risk of acquiring male breast
cancer compared to the general population. This is most likely due to the
hormonal changes that induce gynecomastia, which also raise the risk of male
breast cancer.
If you’re uncomfortable about the appearance of your chest
in public and do not feel comfortable in your skin, don’t be hesitant to talk
about your issue openly and talk to your health care provider. To avoid any
future complications and the development of other mental and physical health
issues, it is advised that you get treatment as soon as you begin to notice the
symptoms of gynecomastia.






Comments
Post a Comment